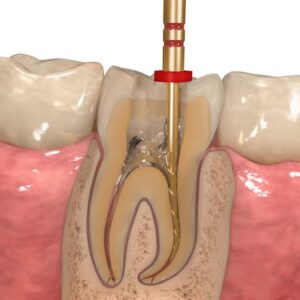
Disinfection of root canal system is defined as destruction of pathogenic micro-organisms, presupposes previous adequate removal of pulp tissue and debris cleaning and enlarging of the canal by biochemical means, and clearing of its contents by irrigation.
These are following methods of disinfecting root canal:
1. Physical i.e., LASER, X-rays, UV rays and diathermy.
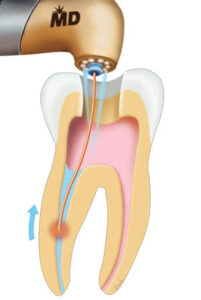
2. Chemical ie, formocresol, eugenol, crestin and poly antibiotic paste.
3. Combination of both i.e., electrosterilization
1. Physical :
a. Diathermy :
1. It uses high frequency current to elevate the temprature of tissue locally or of body in general.
2. The frequency used is 29,000.
3. There is a disadvantage that, it causes, ankylosis of tooth.
b. LASER: It use neodymium yhrium aluminium garnet.
2. Chemical :
a. Intracanal medicamerts:
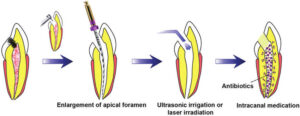
-The intracanal medicamerts are placed in root canal with absorbent paper points.
– Paste is applied on file and rubbing against wall is also a method.
-Ideally one week, not more than two weeks.
-Liquid preparation applied in absorbent paper points and is placed in, root canal. In pulp chamber a cotton pellet soaked in intra canal medicaments is placed and access cavity is sealed.

-Liquid preparation shows vaporization and thus diffuse in root canal.
b. Poly antibiotic paste :
The poly antibiotic pastes are:
1. PBSC, i.e. potassium penicillin bacitracin streptomycin sulphate caprylate sodium paste.
2. PBSN, i.e. Potassium perricillin G bactracin streptomycin sulphate nystatin paste.
3. NBPN, i.e. Neomycin sulphate Bacitracin polymixin sulphate nystatin paste.
Advantage
1. Few sittings are required for disinfection of root canal, as compared to crestin and other disinfectants.
2. Rapid disinfection of root canal save operators time and time of patient.
3. Acute symptoms subsides fast. Periapical tissues heal rapidly and non-irritating to periapical tissues
4. Renders uncertainty and gives dentist a confidence in treatment of periapical disease.
5. No need of frequent changing of root canal dressing Poly antibiotic paste has action for 7 days.
Disadvantages :
1. Paste confined to root canal and not to periapical tissue so no sensitivity.
2. Paste has hydrophobic silicon fluid so no chance of absorption in blood and devitalisation of sensitivity.
3. Devitalisation of resistant microorganism is not possible.
3. Combination of both :
Electosterilization:
– It is the simultaneous application of suitaible medicament and direct current.
-The medicament may be an electrolyte.
Principle: It is based on physical and chemical method sterilization of root canal.
Appratus :
1. It has two electrodes and one electrolyte.
2. One electrode has placed in root canal and other in patients hand.
3. The electric current is passed through electrolyte of 20-30 volts.
4. Rheostat for controlling current.
5. Electrolyte i.e., Iodine solution or 1% NaCl.
Mechanism of Action :
1. Electrolytes dissociates into ions in a salt.
2. These ions are destructive to micro-organism.
Steps :
1. Isolate with rubber dam.
2. Metallic articles like rings, bracelet are remove, since short circuit occurs.
3. Electrode held by patient in hand must contact skin broadly.
4. Root canal is prepared, dry it after irrigation.
5. Flood the root canal with zinc iodine solution. Plumb solution to apex with syringe.
6. Electrode placed in root canal is of zirconium point. Proper size is selected which reaches till apical 1/3.
7. Hand electrode is held firmly by patient.
8. Current is increased slowly only till patient has tingling sensation.
Indication :
1. When rapid disinfection is required.
Disadvantage
1. Expensive.
2. Tooth discolouration.
3. No advantage over simple method.