It is the pathological wearing away of tooth substance through abnormal mechanical process.
ETIOLOGY :-
-Use of abrasive dentifrices, horizontal toothbrushing, habitual opening of bobby pins.
-Holding nails or pins between teeth, e.g. in carpenters, shoemakers or tailors.
-Improper use of dental floss and tooth picks.
TYPES :-
-Toothbrush abrasion-described below. –
Habitual abrasion .
• Habitual pipe smoker may develop abrasion on the incisal edges of lower and upper anterior teeth.
•Improper and habitual use of tooth prick or dental floss can cause abrasion on the proximal surface of teeth.
-Occupational abrasion-it occurs when objects and instrument are habitually held between the teeth by people during working.
• Ritual abrasion-it is mainly seen in Africa.
CLINICAL FEATURES :-
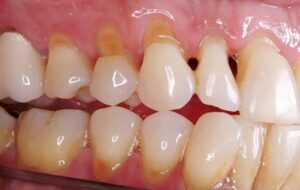
Toothbrush Injury –
• Sites-it usually occurs on exposed surfaces of roots of teeth.
• Mechanism-it occurs due to back and forth movement of brush with heavy pressure causing bristles to assume wedge shaped arrangement between crown and gingiva.
. Appearance- in horizontal brushing there is usually a V shaped or wedge shaped ditch on the root at cementoenamel junction. It is limited coronally by enamel.
• Side-it is more commonly seen on left side of right handed persons and vice versa.
•Symptoms- patient develops sensitivity as dentin becomes exposed.
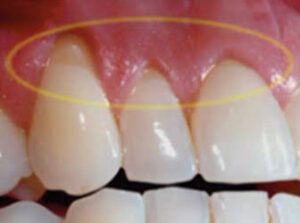
Signs :-
•The angle formed in the depth of the lesion as well as that of enamel edge is a sharp one.
• Cervical lesions caused purely by abrasion have sharply defined margins and a smooth, hard surface.
•The lesion may become more rounded and shallow, if there is an element of erosion present.
•Exposed dentin appears highly polished.
• Exposure of dentinal tubules and consequent irritation of the odontoblastic processes stimulates secondary dentin formation which is sufficient to protect the pulp from clinical exposure.
Dental Floss or Tooth Prick Injury :-
•Cervical portion of proximal surfaces, just above the gingival margin, is affected.
•Grooves on distal surface are deeper than on mesial surface.
RADIOGRAPHIC FEATURES :-
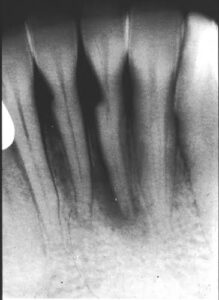
Toothbrush Injury –
•Location-radiolucent defect at the cervical level of teeth.
•Shape-well defined semilunar shape, with borders of increasing density.
•Pulp-pulp chamber may be partially or fully sclerosed in severely affected teeth.
Dental Floss Injury :-
Appearance-narrow semilunar grooves in the interproximal surfaces of teeth near cervical area
Management :-
•Examination and modification of teeth cleaning habits will be indicated.
•Elimination of causative agent.
•Restoration, for esthetics and to prevent further tooth wear.