About Dr. Gourav Sharma:

Senior Painless Dental Surgeon in Para Military Hospital
Para Military ITBP Hospital, Indo-Tibetan Border Police Force, Government of India, Shivpuri, Madhya Pradesh
2013 to 2017 Shivpuri, Madhya Pradesh
Modern Painless techniques and Sophisticated medicines in Para Military Hospital.

Apollo Hospital Senior Associate Dental Surgeon
Physical Treatment & Online Dental Consultation to the Patients.
 Lecturer & Dental Surgeon Mansarovar Hospital & Research Center
Lecturer & Dental Surgeon Mansarovar Hospital & Research Center
Lecturer & Dental Surgeon in Mansarovar Hospital and Research Center Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh
- 2011 to 2012
 Senior Painless Dental Surgeon.
Senior Painless Dental Surgeon.
2011 to current in own Parthsarathy Dental Clinic Shivpuri, Madhya Pradesh
 Senior Healthcare Consultant at Practo
Senior Healthcare Consultant at Practo
2021 to current with own clinic online and Physical support to the Patients
- Provide online support to the patients, when the problem does not report as complete or require Dentist assistance.
Dilaceration
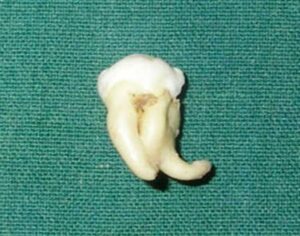
Dilaceration refers to angulations or sharp bends or curve in the roots and crowns of the teeth.
Etiology
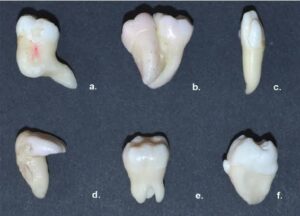
Trauma-mechanical trauma to calcified portion of partially formed teeth results in dilaceration. The portion formed after accident is in different direction causing the dilaceration.
Developmental defect.
Obstacle to the normal direction of growth.
Clinical features
Sex and site-it is found equally in both sexes. It is most commonly found in maxillary incisors.
Appearance-curve or bending occurs anywhere along the length of tooth, sometimes at cervical portion or midway along the root or even just at the apex of root.
Significance
Sometimes, angles are so acute that a tooth does not erupt.
If the defect is in the crown of an erupted tooth. the angular distortion will be recognized.
Radiographic features
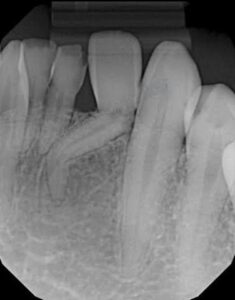
Location-it will show angular distortion of unusuala relationship between coronal and radicular portion of the tooth, on either side of defect.
Appearance
If the malformed teeth bend over the fold the defect will be obscured..
• If the root bends mesially or distally condition will clearly appear on radiograph.
When it is tilted buccally or lingually, dilacerateda portion will appear at apical end as a roundeda opaque area with dark shadow in central region cast by apical foramen. Periodontal space about this is evidenced as a radiolucent halo.
Differential diagnosis
Fused root-in this case, you will be able to find two different root canals.
Condensing osteitis-the tooth is non-vital in case of condensing osteitis.
Management
Difficulty at the time of extraction.
Dilacerated crown has to be restored with crown to improve esthetics and function and to preclude dental caries and periodontal disease.