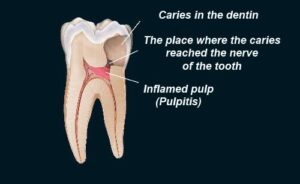
Extensive acute inflammation of the tooth dental pulp is a frequent sequel of focal reversible pulpitis of teeth.
Causes of Dental acute Pulpitis :-
It usually occurs in a tooth with a large carious lesion or a defective restoration dental cavity, where there has been recurrent dental caries.
Tooth Pulp exposure due to faulty cavity preparation sometimes by non licensed dental practitioners.
Blow to tooth with subsequent damage to teeth pulp.
Cracked tooth syndrome.
It may occur as acute exacerbation of chronic inflammatory process .
Recurrent caries in a tooth around old dental restoration.
Clinical features of dental acute pulpitis:-
• Severe pain is elicited by thermal changes and pain persists even after thermal stimulus disappears or has been is removed. Sometimes dentist also proper procedure to identify infected tooth.
• As greater proportion of the pulp becomes involved with intrapulpal abscess formation, the teeth pain may become even more severe and is often described as lancinating type.
It may be continuous and its intensity may be increased when the patient lies down.
The application of heat may cause acute exacerbation of dental pain and the tooth reacts to the electric pulp vitality tester by Dentist at a lower level of current than adjacent normal teeth.
Severe pain is more opt to be present when the entrance to the diseased pulp is not wide open. Pressure increases because of lack of escape of inflammatory exudate and there is rapid spread of inflammation throughout the teeth pulp with pain and necrosis.
• If a cavity is large then the inflammatory process does not tend to spread rapidly throughout the pulp. In this cases, the dental pain felt is dull, throbbing ache, but tooth is still sensitive to thermal changes.
The patient with acute pulpitis is extremely uncomfortable and at least mildly ill. He is usually apprehensive and desirous of immediate attention.
Histologic features :-
• Continued vascular dilatation accompanied by the accumulation of edema fluid in the connective tissue surrounding the tiny blood vessels.
The pavementing of polymorphonuclear leukocytes becomes apparent along the walls of the vascular channels and these leukocytes rapidly migrate through the endothelium lined structure in increasing numbers.
Collection of white blood cells are found beneath the area of carious penetration and odontoblasts in this area are destroyed.
There may be localized destruction of dental pulp tissue and formation of pus resulting in condition known as pulp abscess. It contains pus arising from breakdown of leukocytes and bacteria as well as from digestion of tissue. In tissue section it appears as a small void surrounded by a dense band of leukocytes.
In some cases within a few days, the acute inflammation spreads to involve most of the pulp so that neutrophilic leukocytes fill the pulp. The entire odontoblastic layer degenerates. As pulp is closed, there is rise in pressure and the entire pulp tissue undergoes rapid disintegration, forming numerous small abscesses. Eventually the entire pulp undergoes liquefaction and necrosis which is called as acute suppurative pulpitis.
Management :-
In early stages pulpotomy (removal of the coronal pulp) and placing material that favors calcification such as calcium hydroxide over the entrance of root canals by Dental Surgeon.
Root canal filing with inert material like gutta percha by Dentist.