The angina pectoris is a symptom complex caused by transient myocardial ischaemia and constitutes a clinical syndrome rather than a disease.
Types
1. Nocturnal.
2. Unstable
3. Prinzmetal’s
4. Intractable.
Causes :
i. Athrosclerosis
ii. Aortic stenosis
iii. Hypoxemia.
Clinical Features :
a. The most important feature is chest pain on exertion and pain subsides at rest.
b. Pain is mostly non serious, vague usually on left side. The pain may radiate to the medial side of left arm, left side of neck and jaws.
c. Many times there is only chest discomfort and or breathlessness or perspiration.
d. Factors precipitating angina
i. Physical exertion
ii. Heavy meals
iii. Cold exposure
iv. Intense emotion
v. Pressure or defecation
vi. Lying flat (rarely)
vii. Vivid dreams.
Diagnosis :
i. ECG shows that S-T segment is decreased.
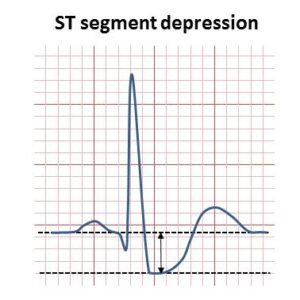
ii. Stress test or Treadmill test.

iii. Cardiac angiography.
iv. Cardiac enzyme study like SGPT, CPK and LDH
Management :
It is divided into three phases:
1. General measures
II. Pharmacological treatment
III Invasive treatment.
1. General Measures :
a. Do not smoke
b. Aim at ideal body weight
c. Take regular exercise
d. Avoid severe exertion, vigorous exercise and exercise in cold weather
e. Take sublingual nitrate before taking exertion that may induce angina.
II. Pharmacological Treatment :
The following agents are used with successful outcome.
A. Antiplatelet agents:
a. Aspirin is used usually in dose of 75 to 150mg daily.
b. Clopidogrel is used along with or without aspirin at dose of 75mg daily.
B. Anti-anginal Agents :
a. Sublingual glycertrinitrate effectively abort anginal attack by causing coronary vasodilatation and reducing preload and cardiac output.
b. Beta-blockers improve cardiac efficiency and reduce oxygen consumption. Cardioselective agents like atenolol 25 to 50mg, metoprolol 200 mg daily can be used.
c. Calcium channel antagonists, i.e. amlodipine, lacidine. They are the vasodilators and lowers myocardial oxygen demand by reducing blood pressure and myocardial contractility.
d. Potassium channel opener, i.e. nicorandil has atrial and venous dilatation property which does not exhibit tolerance.
Invasive Treatment :
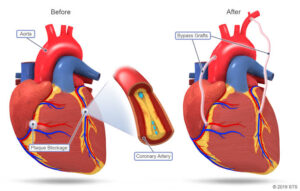
a. *Percutaneous coronary *intervention or percu- taneous transluminal coronary angioplasty is done.
b. Coronary artery bypass grafting is done.