Crossbite Correction
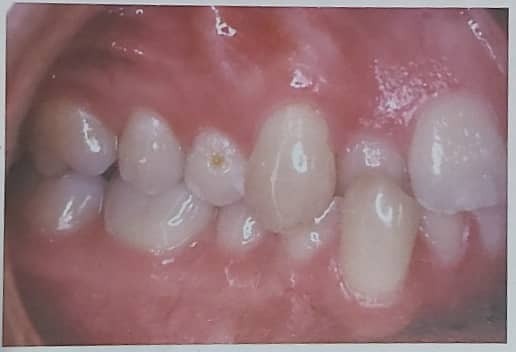
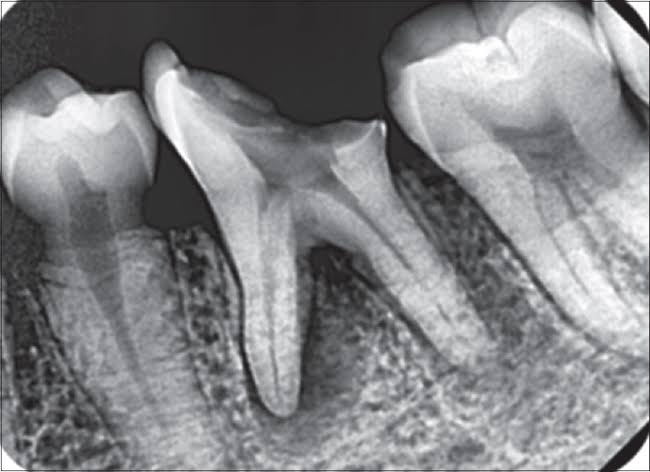
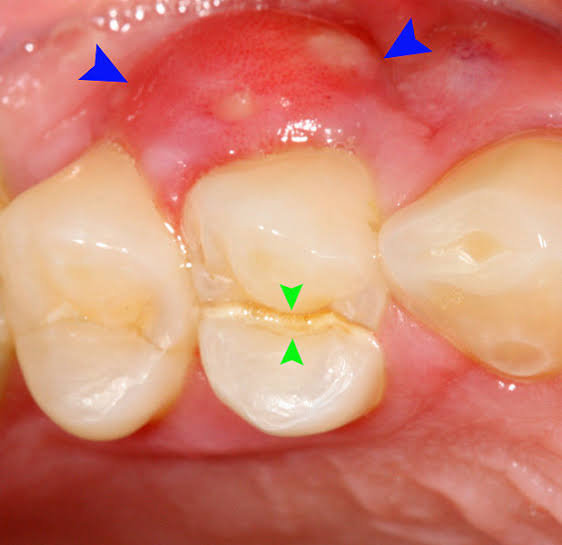
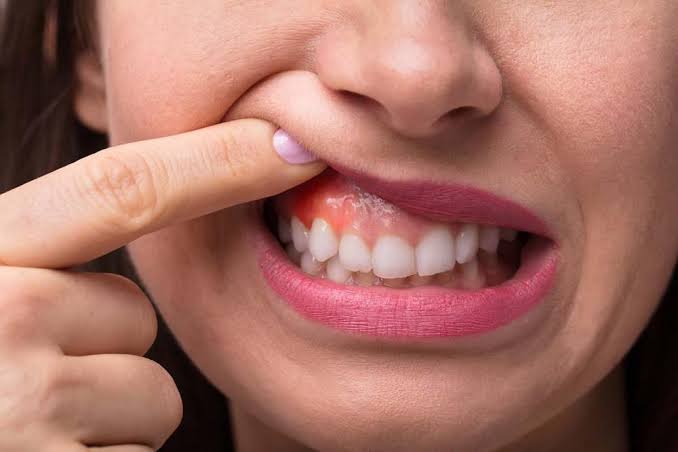
CROSSBITE CORRECTION It is important to correct posterior crossbites and mild anterior crossbites (one or two displaced teeth) in the first stage of treatment. Severe anterior crossbites (all the teeth), in contrast, are usually not corrected until the second stage of conventional treatment or might remain pending surgical correction. For both posterior and anterior crossbites, […]
Crossbite Correction Read More »