Dentinal Sclerosis
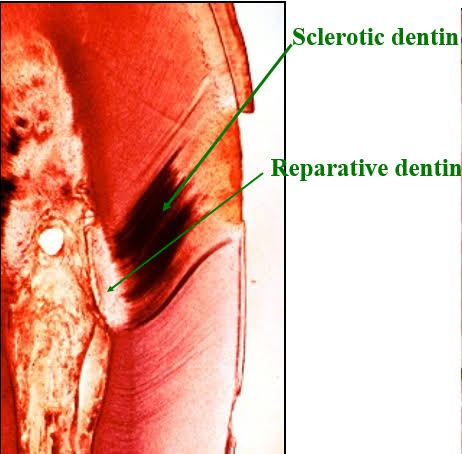
Dentinal Sclerosis Sclerosis of primary teeth dentin is a regressive alteration in tooth substance that is characterized by calcification of the tooth dentinal tubules. It occurs not only as a result of injury to the teeth dentin by dental caries or abrasion but also as a manifestation of the normal aging process. For many years […]
Dentinal Sclerosis Read More »