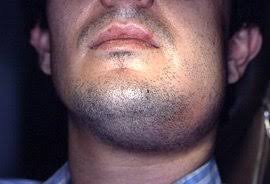
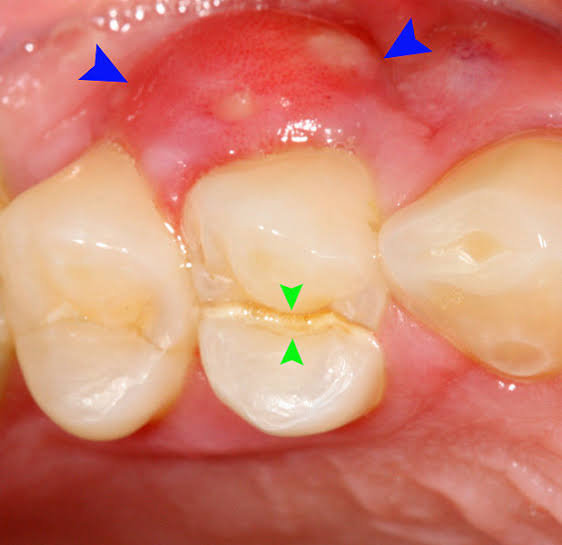
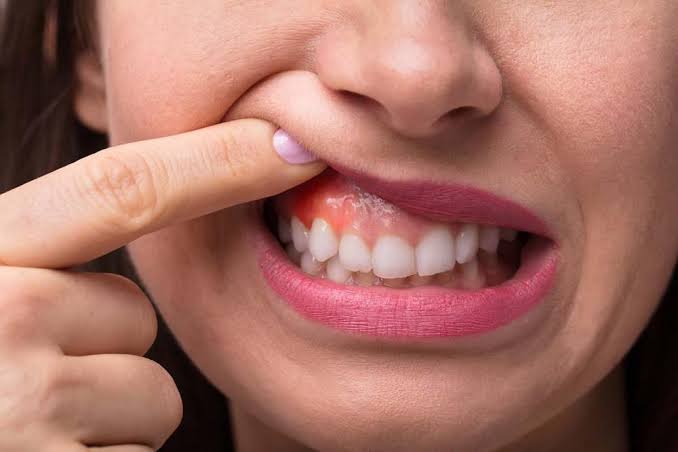
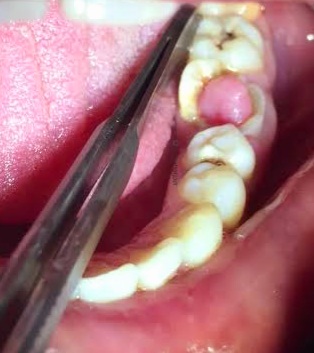
Ludwig’s Angina
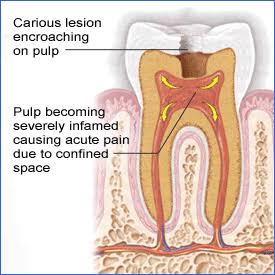
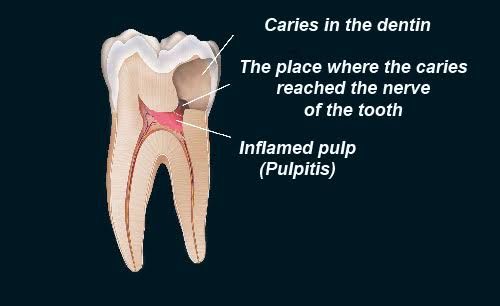
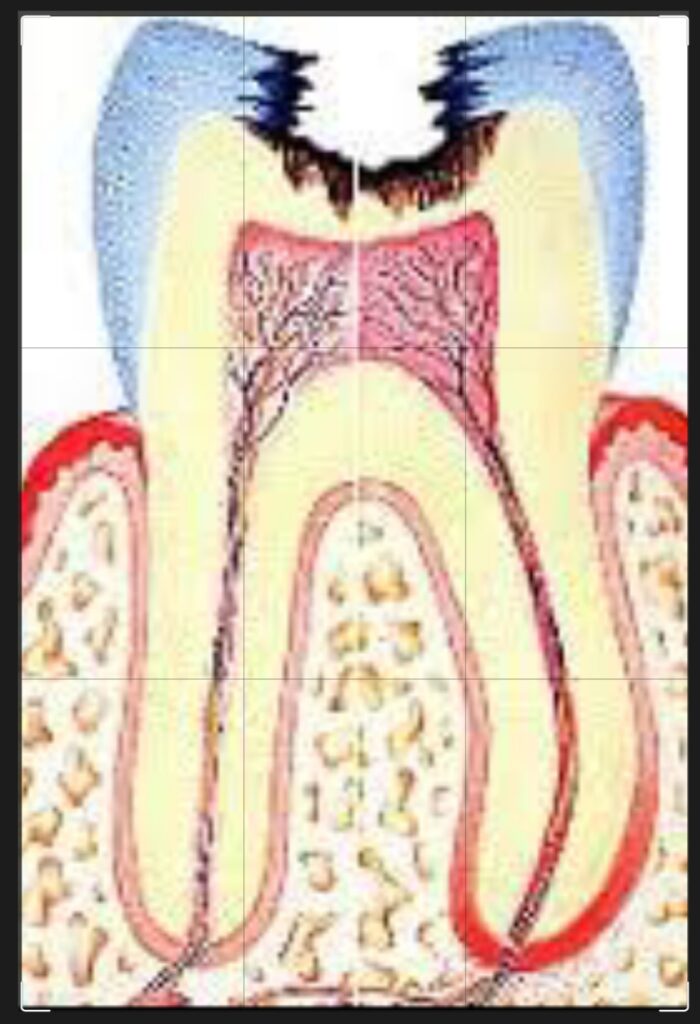
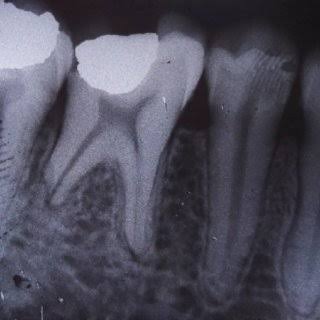
It is a condition which was first described by Ludwig in 1936. The word angina means sensation of choking or suffocation. It is the most commonly encountered neck space infection. This condition may be defined an overwhelming, rapidly spreading, septic cellulitis involving submandibular, submental and sublingual spaces bilaterally. Etiology :- Odontogenic infection-it is usually an […]