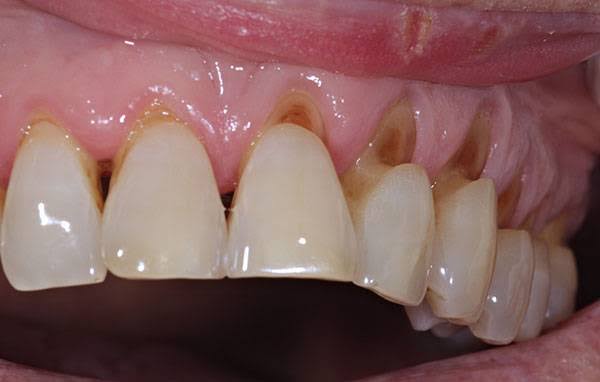
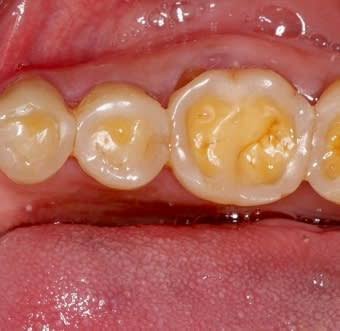
Abrasion
It is the pathological wearing away of tooth substance through abnormal mechanical process. ETIOLOGY :- -Use of abrasive dentifrices, horizontal toothbrushing, habitual opening of bobby pins. -Holding nails or pins between teeth, e.g. in carpenters, shoemakers or tailors. -Improper use of dental floss and tooth picks. TYPES :- -Toothbrush abrasion-described below. – Habitual abrasion . […]