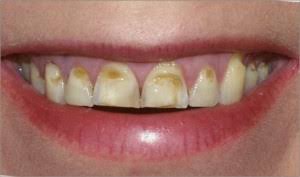
It is the loss of tooth substance by chemical process that does not involve known bacterial action. Dissolution of mineralized tooth structure occurs upon contact with acids. Erosion is a chemical process in which the tooth surface is removed in the absence of plaque.
TYPES (DEPENDING UPON ETIOLOGY) :-
• Intrinsic erosion that occurs due to intrinsic cause,
e.g. gastroesophageal reflux, vomiting.
• Extrinsic-erosion occurring from extrinsic sources,
e.g. acidic beverages, citrus fruits.
ETIOLOGY :-
•Local acidosis in periodontal tissue from damage due to traumatogenic occlusion.
• Chronic vomiting-complete loss of enamel on lingual surfaces of teeth through dissolution by gastric hydrochloric acid. Vomiting can also occur in alcoholics, peptic ulcer, gastritis, pregnancy and drug side effect.
•Acidic foods and beverages :-
• Large quantities of highly acidic carbonated beverages or lemon juice can produce erosion.
• Most of the fruits and fruits juices have a low pH and can cause erosion.
•Frequent consumption of carbonated drinks, which are acidic in nature, may result in erosion of teeth.
•Anorexia nervosa-it induces chronic vomiting often after bouts of uncontrolled eating that is interspersed
between periods of starvation, because of inner rejection of food.
•Occupational- workers involving in manufacturing of lead batteries, sanitary cleaners or soft drinks can develop erosion.
CLINICAL FEATURES :-
Sites :-
•It occurs most frequently on labial and buccal surfaces of teeth; some times may occur on proximal surfaces of teeth.
•Usually confined to gingival thirds of labial surface of anterior teeth.
•Erosion may involve several teeth of dentition.
• From extrinsic source, it causes erosion on labial and buccal surface and from intrinsic source, it causes erosion on lingual or palatal source.
•Appearance it is usually a smooth lesion which exhibits no chalkiness.
•Symptoms-loss of enamel often causes hyper- sensitivity in teeth and may also trigger secondary dentin formation.
Signs :-
• Loss of tooth substance is manifested by shallow, broad, smooth, highly polished and scooped out depression on enamel surface adjacent to cementoenamel junction.
•There may be pink spot on tooth which is attributable to the reduced thickness of enamel and dentin making the pink hue of pulp visible .
•Erosive lesions cause ‘cupping’ in dentine.
•When erosion affects the palatal surfaces of upper maxillary teeth, there is often a central area of exposed dentine surrounded by a border of unaffected enamel .
•In most cases, it results in little more than a loss of normal enamel contour, but in severe cases, dentine or pulp may be damaged.
RADIOGRAPHIC FEATURES :-
It appears as radiolucent defect in the crown margins may be well defined or diffuse.
MANAGEMENT :-
• In a patient where loss of tooth surface is essentially caused by erosive fluids, advise regarding diet and use of sugar free chewing gum. Prescription of a fluoride mouthwash is certainly indicated here.
•Modifying brushing habits and restoration of the defect, usually by glass inomer cement.
•For systemic management of vomiting, patient should be referred to the physician.