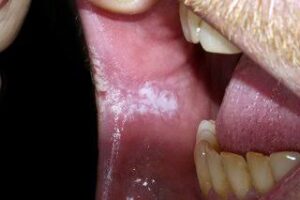
Leukoplakia is a white patch in the mouth. Leukoplakia is a condition in which thick, white or grayish patches form usually inside the mouth.
Etiology of Leukoplakia :
The common predisposing factors of leukoplakia are:
1.Tobacco:
It is used by large number of people in various forms such as smoking of cigarette. Cigar, biddies and pipes. All these types of tobacco habits are important for development of leukoplakia. It is believed that during smoking a large amount of tobacco end products are produced in oral cavity. The products in association with heat cause severe irritation to oral mucus membrane and finally result in development of leukoplakia.
2.Alcohol:
Many people-develop leukoplakia that consume alcohol leukoplakia as well as use tobacco in some form.
3. Candidiasis:
Chronic candidal infections are associated with leukoplakia.
4.Dietary Deficiency:
Deficiency of vitamin A causes metaplasia and hyperkeratinization of epithelium which may result in development of leukoplakia.
5 Syphilis:
The syphilitic infections play minor role in causation of leukoplakia.
6.Hormonal Imbalance:
Imbalance or dysfunction of both male and female sex hormones causes keratogenic changes in oral epithelium. These changes lead to the development of leukoplakia.
Sign and Symptoms :
Usually the lesion occurs in 4th 5th 6th and 7th decades of life.
Buccal mucosa and commissural areas are most frequent affected sites followed by alveolar ridge,tongue, lip, hard and soft palate, etc.
Oral leukoplakia often present solitary or multiple white patches.
The size of lesion may vary from small well localized patch measuring few millimeters in diameter.
The surface of lesion may be smooth or finely wrinkled or even rough on palpation and lesion cannot be removed by scrapping.
The lesion is whitish or grayish or in some cases it is brownish yellow in colour due to heavy use of tobacco.
In most of the cases these lesion are asymptomatic, however, in some cases they may cause pain, feeling of thickness and burning sensation, etc.
Diagnosis :
Diagnosis is based on the investigation. Biopsy is the best method in making diagnosis. Both incisonal and excisonal biopsy is done. When histopathology of leukoplakia is to be done, it shows following features which helps in making diagnosis:
Presence of hyperplasia
Atrophy of epithelium
Acanthosis is present
Basal cell hyperplasia
Presence of epithelial dysplasia.
Differential Diagnosis :
1.Lichen planus:
Distinguished by frequent occurrence of multiple lesions and presence of Wickham’s straie.
2. Syphilitic mucus patches:
Features like split papule are present.
3. Discoid Lupus Erythematosus:
Central atrophic area with small white dot and slightly elevated borders.
4. Psoriasis:
Auspitz’s sign is positive.
5. Leukoedema:
It occurs on buccal mucosa covering most of oral surface of cheek extending on labial mucosa.
6. Hairy leukoplakia corrugated leukoplakic lesion:
Occuring on lateral and ventral surface of tongue in patient with AIDS.
7.Cheek Biting lesion:
Careful history elicit cause and promote proper diagnosis.
Prognosis :
Prognosis is quite fair.
Rate of regression is higher when tobbaco habit is discontinued.
Treatment :
I Vitamin therapy:
Vitamin A is given i.e., 4000 IU orally, Parentrally or topically.
II Anti-oxidant therapy:
Beta carotene supple- mentation is beneficial for treatment of oral leukoplakia.
III Nystatin therapy is given in candidal leukoplakia 500,000 IUBD.
IV. Vitamin B complex.
IV. Estrogen is given in some cases.