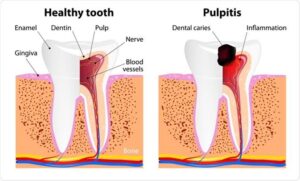
Classification of pulp disease :
1. Pulpitis (Inflammation) :
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the tooth pulp, the soft inner tissue of your teeth.
A. Reversible Dental pulpitis :
Pulpitis is reversible if you identify it early. Your dentist will treat the cause and expect the symptoms to resolve.
1. Symptomatic (acute).
The main sign that the tooth pulpitis has progressed to irreversible pulpitis is a lingering sensitivity to heat or cold in teeth.
2. Asymptomatic (chronic).
B. Irreversible Dental pulpitis :
The main sign that the tooth pulpitis has progressed to irreversible pulpitis is a lingering sensitivity to heat or cold.
1. Acute :
a. Abnormally responsive to cold by tooth.

b. Abnormally responsive to heat by tooth.

2. Chronic :
a. Asymptomatic with dental pulp response.
b. Hyperplastic pulpitis.
c. Internal resorption.
II. Pulp Degeneration
a. Calcific (Radiographic diagnosis)
b. Others (Histopathologic diagnosis)
III. Pulp Necrosis
Acute Dental Pulpitis :
Extensive acute inflammation of pulp teeth is a frequent sequelae of focal reversible pulpitis.
Etiology :
It usually occurs in a tooth with large carious lesion.
Pulp exposure due to faulty cavity preparation.
Blow to tooth with subsequent damage to pulp.
Cracked tooth syndrome.
Acute exacerbation of chronic inflammatory process.
Recurrent caries in a tooth around restoration.
Diagnosis :
Diagnosis is done by the study of patients symptoms and by clinical test :-
Patient complains of pain which is sharp in nature lasts for few seconds and disappears when the stimulus is removed which indicates acute reversible pulpitis.
When the pain is exaggerated and remains for a longer time after the removal of stimuli which indicates acute irreversible pulpitis.
Clinical Features :
Severe pain is elicited by thermal changes and pain persist even after thermal stimulus is removed :-
The pain may be continuous and its intensity may be increased when the patient lies down.
The tooth reacts to the electric pulp vitality tester at a lower level of current than adjacent normal teeth.
The patient with acute pulpitis is extremely uncomfortable and at least mildly ill.
Treatment :
Reversible pulpitis:
In easy cases pulpotomy is done and Ca (OH), is placed over the entrance of root canal which favors calcification.
Root canal filling with inert material like gutta- percha is done.
Irreversible pulpitis:
Pulpectomy is done and placement of intracanal medicament to act as disinfectant or obtundant such as eugenol or cresatin .